Over the past year, names like Ozempic, Wegovy, and Mounjaro have been popping up everywhere—from TikTok influencers to Hollywood red carpets. Marketed as revolutionary treatments for diabetes, these drugs are now being hailed as miracle weight loss solutions. But what’s really behind the hype?
In this article, we break down the science, the results, the risks—and whether these GLP-1 drugs are a shortcut or a slippery slope.
What Are GLP-1 Agonists?
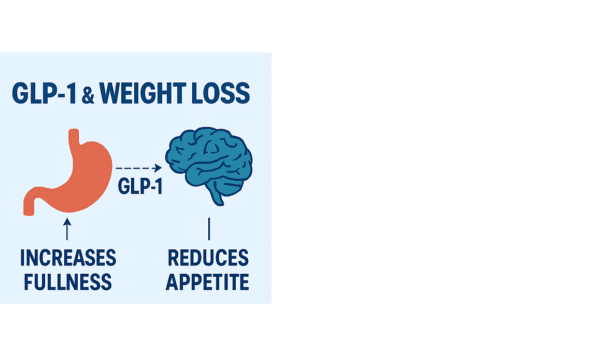
GLP-1 stands for glucagon-like peptide-1, a hormone naturally produced in the gut. It plays a key role in regulating blood sugar levels, appetite, and satiety. GLP-1 receptor agonists are medications that mimic this hormone to help manage type 2 diabetes.
But it turns out, they also dramatically reduce appetite—leading to significant weight loss in many users.
Some of the most talked-about drugs include:
- Ozempic (semaglutide) – approved for type 2 diabetes
- Wegovy (semaglutide, higher dose) – approved for weight loss
- Mounjaro (tirzepatide) – acts on GLP-1 and GIP receptors
How Much Weight Can You Really Lose?
According to clinical studies:
- Wegovy users lost up to 15% of their body weight over 68 weeks.
- Mounjaro users saw losses up to 22% in some trials.
These results rival even bariatric surgery in some cases. The appetite suppression is intense: many users report forgetting to eat or feeling full after just a few bites.
But the effectiveness can vary:
- People with more weight to lose often see bigger changes.
- Lifestyle factors (diet, movement, stress) still matter.
- Stopping the medication often leads to weight regain.
The Side Effects & Controversies

As with any drug, GLP-1 agonists are not without risks. The most common side effects include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue
- Loss of muscle mass
More serious concerns include:
- Potential thyroid tumors (in rodents)
- Pancreatitis
- Gallbladder issues
There’s also a growing ethical debate: Should people take expensive diabetes medications just to lose weight—especially when some diabetics can’t access them due to shortages?
And while the physical changes can be striking, psychological effects like disordered eating, body image issues, and medication dependency are emerging areas of concern.
Are There Natural Alternatives?
For those who prefer not to go the pharmaceutical route, some strategies may mimic the GLP-1 effect naturally:
- High-protein, high-fiber diets (both slow digestion and increase satiety)
- Fermented foods & prebiotics (support gut hormones)
- Intermittent fasting (regulates hunger hormones)
- Cold exposure (may increase GLP-1 sensitivity)
These don’t match the potency of semaglutide, but they come without the same risks or costs.
Real Stories, Real Questions
A growing number of celebrities, influencers, and everyday people have documented transformations with GLP-1 drugs. But behind each success story, there’s a complex emotional and physical journey.
Before jumping on the trend, it’s worth asking:
- Am I ready for the side effects?
- Can I afford this long-term?
- What happens when I stop?
Final Thoughts: Shortcut or Slippery Slope?
There’s no doubt: GLP-1 medications are reshaping the weight loss landscape in America. For many, they’re a game-changer—offering real hope where diets and workouts failed.
But these drugs are not magic pills. They come with trade-offs: side effects, high costs, and the potential for rebound weight gain.
If you’re considering them, speak with a trusted medical professional, understand the long-term implications, and don’t neglect the foundations: nutrition, movement, mindset, and support.
Want to dive deeper into weight loss trends, gut health, or AI-based coaching? You can have a look at the former post about intermittent fasting.